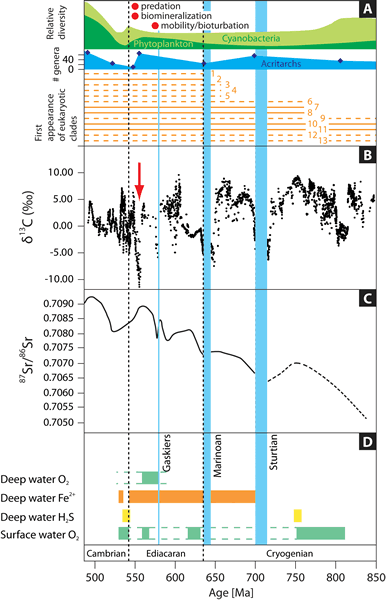
Figure 2.
(A) Compilation showing the emergence of predation (Bengtson and Zhao, 1992), biomineralization (Grotzinger et al., 2000), and mobility (Liu et al., 2010); the relative diversity of cyanobacteria and phytoplankton through time (modified after Moczydlowska, 2008); acritarch diversity; and first appearance of eukaryotic clades. 1—brown algae; 2—animals; 3—haptophytes; 4—diatoms; 5—chrysophyte algae; 6—green algae; 7—lobose amoebae; 8—euglyphid amoebae; 9—fungi; 10—vaucheriacean algae; 11—red algae; 12—dinoflagellates; 13—ciliates (modified after Porter, 2004). (B) Secular variation in the carbon isotopic composition (δ13C) of marine carbonates from 850 to 490 Ma (modified after Halverson et al., 2005; Halverson, 2006). The negative δ13C anomalies characterizing the Sturtian and Marinoan glacial intervals suggest they were globally synchronous. Shuram/Wonoka excursion indicated by red arrow. (C) Seawater 87Sr/86Sr curve for the same interval (data for the Ediacaran period from Sawaki et al., 2010). (D) Summary of marine conditions through the last half of the Neoproterozoic and into the early Cambrian (from Canfield et al., 2008).