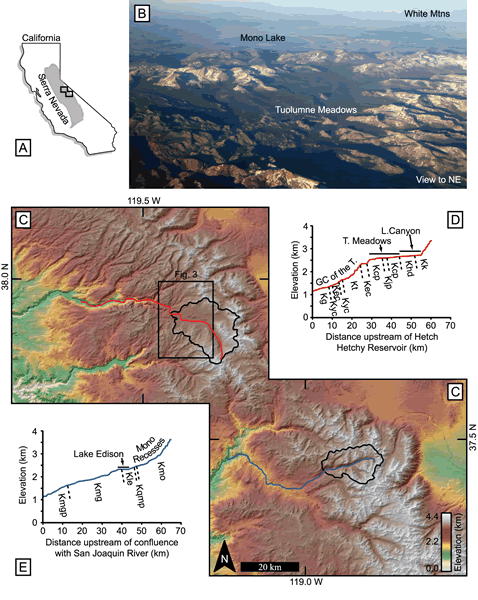
Figure 1.
(A) Outline of California and the Sierra Nevada Mountains, showing panel C’s position. (B) Tuolumne Meadows from the southwest; courtesy of Heidi Crosby. (C) Shaded digital elevation model, colored by elevation, of the central Sierra Nevada. Red and blue lines are the traces of the stream profiles described below in D and E. The drainage basins of the Tuolumne River above Little Devils Postpile (i.e., the Tuolumne Meadows area) and of Mono Creek above Lake Edison (i.e., the Mono Recesses) are shown. The black box indicates Figure 3’s location. (D) Longitudinal profile of the Tuolumne River above Hetch Hetchy Reservoir. The locations of Tuolumne Meadows, the Grand Canyon of the Tuolumne, and Lyell Canyon are indicated. Topography from USGS maps; geology from Huber et al. (1989). Lithologic abbreviations: Kg—Undivided Cretaceous(?) granitic rocks; Kyc—Yosemite Creek Granodiorite; Kec—El Capitan Granite; Kt—Taft Granite; Kcp—Cathedral Peak Granodiorite; Kjp—Johnson Granite Porphyry; Khd—Half Dome Granodiorite; Kk—Kuna Crest Granodiorite. (E) Longitudinal profile of the South Fork of the San Joaquin River above its confluence with the San Joaquin River and continuing up Mono and Golden Creeks. Topography from USGS maps; geology from Bateman et al. (1971) and Lockwood and Lydon (1975). The artificially dammed Lake Thomas Edison is noted. Lithologic abbreviations: Kmgp—Mount Givens Granodiorite, porphyritic; Kmg—Mount Givens Granodiorite, equigranular; Kle—Lake Edison Granodiorite; Kqmp—porphyritic quartz monzonite; Kmo—Mono Creek Granite (from Bateman, 1992).