Page 7 - i1052-5173-29-10
P. 7
100%
Yes responses to
“In your most *
80% recent introductory
course, did your *
students...” * *
All intro courses
60% Earth science * *
Geology *
Oceans
*
40% * *
*
*
* * *
*
20%
*
*
0%
Explore Build Make Work on a Address Analyze Collect Address Discuss a Access Describe Describe Address a
systems predictive systems problem of environ- feedback their own uncertainty change and quantita- a system problem
behavior models visible interest to mental loops data and and that has integrate tive in terms of national
using through the local justice analyze ambiguity multiple info from evidence of its or global
computer causal community issues them to when effects different in support parts and interest
models maps solve a interpreting throughout sources of an relation-
problem data a system argument ships
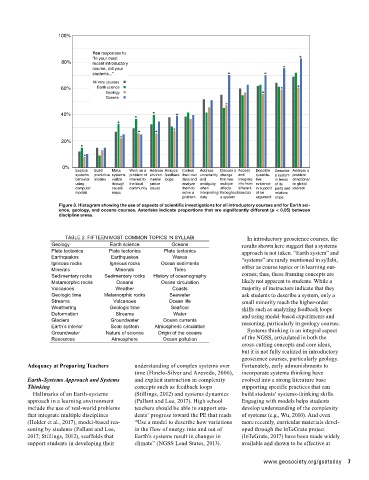
Figure 3. Histogram showing the use of aspects of scientific investigations for all introductory courses and for Earth sci-
ence, geology, and oceans courses. Asterisks indicate proportions that are significantly different (p < 0.05) between
discipline areas.
TABLE 2. FIFTEEN MOST COMMON TOPICS IN SYLLABI In introductory geoscience courses, the
Geology Earth science Oceans results shown here suggest that a systems
Plate tectonics Plate tectonics Plate tectonics approach is not taken. “Earth system” and
Earthquakes Earthquakes Waves “systems” are rarely mentioned in syllabi,
Igneous rocks Igneous rocks Ocean sediments either as course topics or in learning out-
Minerals Minerals Tides
Sedimentary rocks Sedimentary rocks History of oceanography comes; thus, these framing concepts are
Metamorphic rocks Oceans Ocean circulation likely not apparent to students. While a
Volcanoes Weather Coasts majority of instructors indicate that they
Geologic time Metamorphic rocks Seawater ask students to describe a system, only a
Streams Volcanoes Ocean life small minority reach the higher-order
Weathering Geologic time Seafloor skills such as analyzing feedback loops
Deformation Streams Water and using model-based experiments and
Glaciers Groundwater Ocean currents reasoning, particularly in geology courses.
Earth’s interior Solar system Atmospheric circulation
Groundwater Nature of science Origin of the oceans Systems thinking is an integral aspect
Resources Atmosphere Ocean pollution of the NGSS, articulated in both the
cross-cutting concepts and core ideas,
but it is not fully realized in introductory
geoscience courses, particularly geology.
Adequacy at Preparing Teachers understanding of complex systems over Fortunately, early admonishments to
time (Hmelo-Silver and Azevedo, 2006), incorporate systems thinking have
Earth-Systems Approach and Systems and explicit instruction in complexity evolved into a strong literature base
Thinking concepts such as feedback loops supporting specific practices that can
Hallmarks of an Earth-systems (Stillings, 2012) and systems dynamics build students’ systems-thinking skills.
approach in a learning environment (Pallant and Lee, 2017). High school Engaging with models helps students
include the use of real-world problems teachers should be able to support stu- develop understanding of the complexity
that integrate multiple disciplines dents’ progress toward the PE that reads of systems (e.g., Wu, 2010). And even
(Holder et al., 2017), model-based rea- “Use a model to describe how variations more recently, curricular materials devel-
soning by students (Pallant and Lee, in the flow of energy into and out of oped through the InTeGrate project
2017; Stillings, 2012), scaffolds that Earth’s systems result in changes in (InTeGrate, 2017) have been made widely
support students in developing their climate” (NGSS Lead States, 2013). available and shown to be effective at
www.geosociety.org/gsatoday 7