Page 39 - i1052-5173-29-6
P. 39
Q Q
no
known
silexite granodiorite igneous granodiorite
tonalite rocks tonalite
60 60 60 60
alkali
alkali feldspar quartz monzodiorite feldspar quartz monzodiorite
granite quartz monzogabbro granite LG quartz monzogabbro
granite granite
quartz quartz diorite quartz diorite
alkali feldspar quartz gabbro quartz alkali syenite quartz gabbro
syenite quartz anorthosite feldspar quartz anorthosite
10 35 65 90 20 F F 35 F 20
alkali feldspar 20 quartz quartz 20 monzodiorite alkali feldspar quartz quartz C monzodiorite
syenite syenite monzonite monzogabbro syenite syenite monzonite monzogabbro
5 syenite monzonite 5 diorite 5 syenite monzonite 5 diorite
A foid-bearing P gabbro A P gabbro
foid-bearing monzonite anorthosite anorthosite
alkali syenite 10 10 foid-bearing diorite
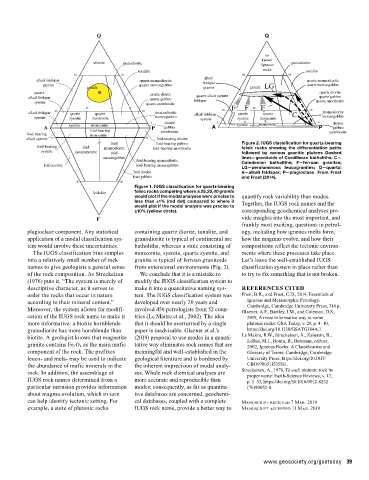
10 50 foid 90 foid-bearing gabbro Figure 2. IUGS classification for quartz-bearing
foid-bearing foid monzodiorite foid-bearing anorthosite felsic rocks showing the differentiation paths
syenite monzosyenite foid followed by various granitic plutons Dashed
monzogabbro lines—granitoids of Cordilleran batholiths; C—
foid-bearing monzodiorite Caledonian batholiths; F—ferroan granites;
foid syenite foid-bearing monzogabbro
LG—peraluminous leucogranites; Q—quartz;
foid diorite A—alkali feldspar; P—plagioclase. From Frost
foid gabbro and Frost (2014).
60 60
Figure 1. IUGS classification for quartz-bearing
foidolite felsic rocks comparing where a 25,25,40 granite
would plot if the modal analyses were precise to quantify rock variability than modes.
less than ±1% (red dot) compared to where it Together, the IUGS rock names and the
would plot if the modal analysis was precise to
±10% (yellow circle). corresponding geochemical analyses pro-
F vide insights into the most important, and
frankly most exciting, questions in petrol-
plagioclase component. Any statistical containing quartz diorite, tonalite, and ogy, including how igneous melts form,
application of a modal classification sys- granodiorite is typical of continental arc how the magmas evolve, and how their
tem would involve these uncertainties. batholiths, whereas a suite consisting of compositions reflect the tectonic environ-
The IUGS classification bins samples monzonite, syenite, quartz syenite, and ments where these processes take place.
into a relatively small number of rock granite is typical of ferroan granitoids Let’s leave the well-established IUGS
names to give geologists a general sense from extensional environments (Fig. 2). classification system in place rather than
of the rock composition. As Streckeisen We conclude that it is a mistake to to try to fix something that is not broken.
(1976) puts it, “The system is merely of modify the IUGS classification system to
descriptive character, as it serves to make it into a quantitative naming sys- REFERENCES CITED
order the rocks that occur in nature tem. The IUGS classification system was Frost, B.R., and Frost, C.D., 2014, Essentials of
according to their mineral content.” developed over nearly 20 years and Igneous and Metamorphic Petrology:
Cambridge, Cambridge University Press, 314 p.
Moreover, the system allows for modifi- involved 456 petrologists from 52 coun- Glazner, A.F., Bartley, J.M., and Coleman, D.S.,
cation of the IUGS rock name to make it tries (Le Maitre et al., 2002). The idea 2019, A more informative way to name
more informative: a biotite hornblende that it should be overturned by a single plutonic rocks: GSA Today, v. 29, p. 4–10,
granodiorite has more hornblende than paper is inadvisable. Glazner et al.’s https://doi.org/10.1130/GSATG384A.1.
biotite. A geologist knows that magnetite (2019) proposal to use modes in a quanti- Le Maitre, R.W., Streckeisen, A., Zanettin, B.,
LeBas, M.J., Bonin, B., Bateman, editors,
granite contains Fe 3O 4 as the main mafic tative way eliminates rock names that are 2002, Igneous Rocks: A Classification and
component of the rock. The prefixes meaningful and well-established in the Glossary of Terms: Cambridge, Cambridge
leuco- and mela- may be used to indicate geological literature and is burdened by University Press, https://doi.org/10.1017/
the abundance of mafic minerals in the the inherent imprecision of modal analy- CBO9780511535581.
rock. In addition, the assemblage of ses. Whole rock chemical analyses are Streckeisen, A., 1976, To each plutonic rock its
proper name: Earth-Science Reviews, v. 12,
IUGS rock names determined from a more accurate and reproducible than p. 1–33, https://doi.org/10.1016/0012-8252
particular intrusion provides information modes; consequently, as far as quantita- (76)90052-0.
about magma evolution, which in turn tive databases are concerned, geochemi-
can help identify tectonic setting. For cal databases, coupled with a complete Manuscript received 7 Mar. 2019
example, a suite of plutonic rocks IUGS rock name, provide a better way to Manuscript accepted 11 Mar. 2019
www.geosociety.org/gsatoday 39